Neil deGrasse Tyson is listed in IMDB as an Actor
https://www.imdb.com/find/?q=neil%20degrasse%20tyson

“This clown appears in IMDB as an actor. LOL — you know, karma apparently demands: They Do Have To Reveal Their Fraud”
“The serpent-gongue-logo NASA crims are raking in $19 billion yearly; they can probably afford to pay quite a few skilled shills and liars to post personal attacks here.”
“If the moon exists and we could be there; we already would be there. Any argument or disagreement at all proves the fraud, its nonexistence, profound impossibility, etc. It would be celebrated, lauded, a freakin daily carnival; instead, we have lies and subterfuge…because it is inescapably a Total Fraud…allllll of it.”
Comments to https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uTChrirK-hw

Karma demands They must reveal Their Fraud
The phrase “Karma demands They must reveal Their Fraud” can be unpacked through the lenses of occult and Kabbalistic teachings. Here’s an explanation of the underlying concepts:
Occult Perspective
- Karma:
- In occult traditions, karma is understood as the law of cause and effect. Every action has a corresponding reaction, and this principle governs the moral and spiritual realms.
- When someone engages in deceit or fraud, the negative energy created must eventually be balanced. This is often seen as a cosmic imperative, where the universe seeks to restore equilibrium.
- Revealing Fraud:
- The idea that deception must eventually come to light is rooted in the belief that truth is a fundamental force. In occult teachings, hidden truths and secrets are thought to possess a kind of energy that demands release.
- Those who engage in fraud are often compelled by karmic forces to reveal their misdeeds, either consciously or unconsciously, as a way to restore balance and correct the energetic disturbances caused by their actions.
Kabbalistic Perspective
- Karma in Kabbalah:
- While Kabbalah doesn’t use the term “karma” per se, it has analogous concepts such as Tikkun (rectification) and Din (judgment). Tikkun involves correcting past mistakes and restoring harmony, while Din refers to the divine judgment that oversees moral order.
- Kabbalistic teachings emphasize that actions, whether good or bad, have spiritual repercussions that must be addressed. Fraud creates a spiritual imbalance that demands correction.
- Revelation of Truth:
- In Kabbalah, the idea of revealing hidden truths is closely tied to the concept of “Or HaGanuz” (the Hidden Light). This divine light, which is concealed in the physical world, represents ultimate truth and wisdom.
- The process of fraud being revealed can be seen as a manifestation of this Hidden Light. As the light exposes darkness, the truth comes to the surface, aligning with the Kabbalistic goal of bringing divine wisdom into the world.
- Divine Justice:
- Kabbalistic teachings also speak of “Sefirot” (divine emanations), specifically the Sefirot of Chesed (mercy) and Gevurah (severity/judgment). The balance between these forces ensures that justice is served.
- Fraud, being an act that disrupts this balance, triggers the divine mechanism of Gevurah, leading to the eventual revelation and correction of the deceitful actions.
Integration of Both Perspectives
The phrase suggests a metaphysical mechanism where the act of fraud generates a need for its exposure. This exposure is driven by the principles of karma and the spiritual laws governing balance and truth. In both occult and Kabbalistic teachings, there is a recognition that hidden wrongs create a form of spiritual debt that must be repaid, often through the forced revelation of the deceit.
Understanding this phrase through these lenses highlights the belief that moral and spiritual laws are inherently self-regulating, demanding transparency and accountability as part of the universal quest for harmony and truth.
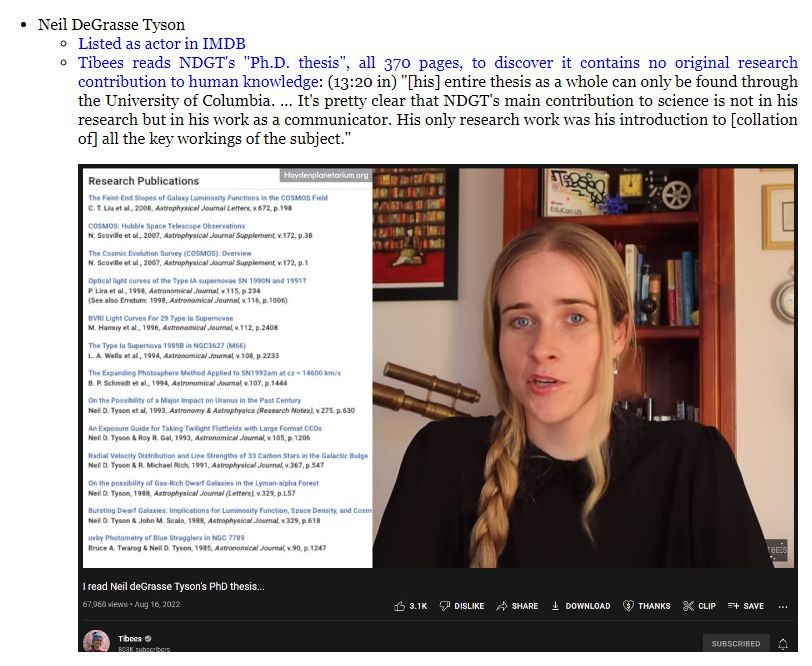
Tibees reveals his PhD thesis (of NdGT)
“It is important not to worship what is known but to question it.” – J Bronowski
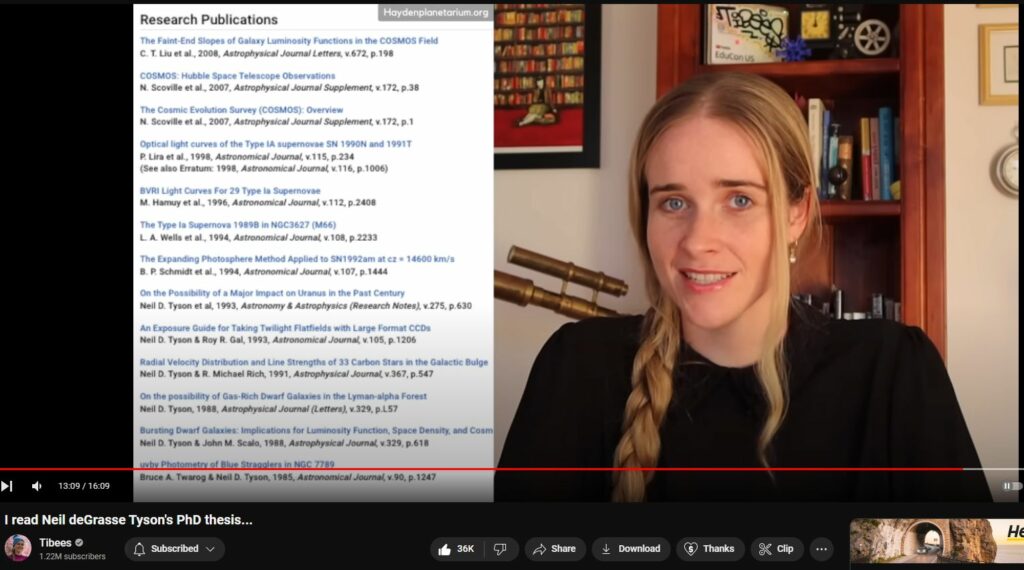
Ph.D. thesis or dissertation must contain an original contribution to human knowledge.
NdGT’s second attempt at Ph.D. thesis was made at Columbia Univ.
Howver, his Ph.D. thesis is only available via special permission/access. — Hiding the clues! (noted most kindly by Tibees at 13:22 into video)
Genuine original contributions should be celebrated, not hidden or made difficult to access!
Instead, Tibess notes it is ‘370 pages of difficult-to-read’ (ostensibly) blib-blab obfuscation.
Tibees: “It’s pretty clear that Neil deGrasse Tyson’s main contribution to science is not in his research but in his work as a communicator: His only ‘research work’ was his introduction to all the key workings of the subject.” 13:33 into video
…and here They are again
Acting/theatre is historically known as Vatican, Jesuit linked and controlled. The theory involving stars, planets, orbits, galaxies, cosmos, black-holes, red-shifts, gravity itself and even the shape (globe vs flat vs concave vs hollow) of realm are all Vatican, Jesuit linked and meddled if not controlled.
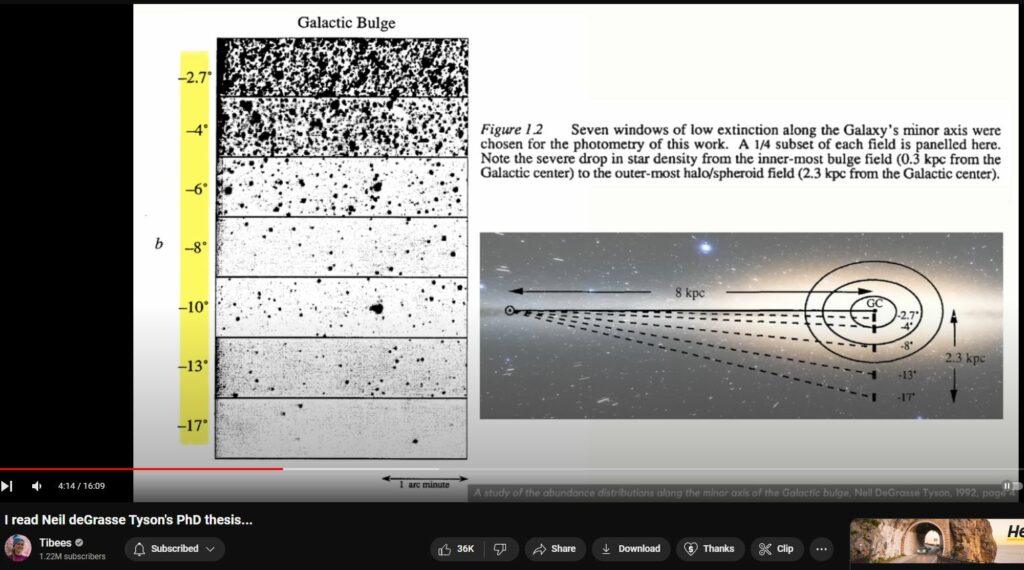
Curiously, NdGT’s PhD serves to counter Olbers Paradox, which gave basis to Edgar Allen Poe’s longest and self-proclaimed greatest work EUREKA in which he peskily reasoned how ‘an Universe of infinite size having infinite stars would present night as bright as day’. NdGT thesis expounds a fall-away of light off-center of galaxies.
Tibees: “”
Hilarious Hallmark
13 Research papers attributed to NdGT
Houston, we are way beyond problem…
“‘Doing science’ means making incremental changes to models of how things work.” Tibees 7:37 into https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=l7f4MSSkDp4
Olbers’ Paradox: Why is the Night Sky Dark?
Have you ever gazed up at the night sky and wondered why it isn’t brilliantly illuminated by countless stars? This question, deceptively simple, puzzled astronomers for centuries and is known as Olbers’ Paradox.
The Paradox Explained
Olbers’ Paradox is named after Heinrich Wilhelm Olbers, a German astronomer who popularized this enigma in the early 19th century, though it was considered by earlier thinkers such as Johannes Kepler and Edmund Halley. The paradox asks: if the universe is infinite, eternal, and uniformly filled with stars, why is the night sky dark?
Here are the key elements of the paradox:
- Infinite Universe: If the universe extends infinitely in all directions, then every line of sight should eventually end at a star.
- Uniform Distribution: Stars are evenly distributed throughout the universe.
- Eternal Universe: The universe has existed forever, giving light from even the most distant stars time to reach us.
Given these conditions, the night sky should be as bright as the surface of the Sun because every point in the sky would be covered by a star. Yet, we observe a predominantly dark night sky. Why?
Solutions to the Paradox
Several explanations have been proposed to resolve Olbers’ Paradox:
- Finite Age of the Universe: The most accepted solution comes from the understanding that the universe is not eternal. The Big Bang theory suggests that the universe is around 13.8 billion years old. This means we can only see the light from stars whose light has had time to reach us. Thus, the observable universe is finite.
- Expansion of the Universe: The universe is expanding, causing distant stars and galaxies to move away from us. Due to this expansion, their light is redshifted into longer, less energetic wavelengths, eventually becoming undetectable to the naked eye.
- Absorption by Interstellar Dust: Initially, it was thought that interstellar dust might block the light from distant stars. However, this dust would eventually heat up and radiate energy, failing to keep the sky dark.
- Finite Number of Stars: While the universe may be vast, the number of stars is not infinite. There are vast empty regions of space, and the density of stars decreases with distance.
Modern Cosmology and Olbers’ Paradox
The resolution of Olbers’ Paradox aligns with modern cosmological principles. The finite age of the universe and its continuous expansion are key factors. Additionally, the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB) gives us a glimpse into the early universe, showing that the universe was once much hotter and denser. As the universe expands, this radiation cools, contributing to the darkness we see in the night sky.
Conclusion
Olbers’ Paradox highlights the importance of questioning and understanding the universe’s nature. It serves as a reminder of the dynamic and ever-evolving field of cosmology. The dark night sky, far from being mundane, tells the story of a finite, expanding universe that began with the Big Bang.
For further reading on Olbers’ Paradox and related cosmological concepts, check out these sources:
- NASA: The Expanding Universe
- Scientific American: Why is the night sky dark?
- Cosmology and Astrophysics: Olbers’ Paradox

https://wp.conspira.org/2024/06/the-poesoning-of-edgar-allen/
Exploring Edgar Allan Poe’s “Eureka”: A Challenge to Jesuit and Vatican Cosmology
Edgar Allan Poe, widely celebrated for his gothic tales and poetry, considered his prose poem “Eureka” his greatest work. Published in 1848, “Eureka” presents Poe’s vision of the universe, which starkly contrasts with the established cosmological views of his time, particularly those supported by the Jesuits and the Vatican. Poe’s bold assertions in “Eureka” not only questioned the nature of the universe but also challenged the foundational principles of contemporary cosmology.
The Essence of “Eureka”
“Eureka” is a complex and ambitious work, blending elements of metaphysics, cosmology, and poetic prose. In it, Poe postulates an interconnected, finite universe that originated from a single primordial particle through a divine act. This view directly opposes the then-dominant belief in an infinite and eternal universe, which had significant support from both religious and scientific authorities.
Key aspects of Poe’s cosmology in “Eureka” include:
- A Finite Universe: Poe argued that the universe is finite in both space and time. This was a revolutionary idea at a time when many believed in an infinite cosmos.
- Big Bang-like Origin: Poe described a cosmic genesis that bears a striking resemblance to what we now know as the Big Bang theory, suggesting that the universe expanded from a singularity.
- Unity of Matter and Spirit: Poe proposed a profound unity between matter and spirit, suggesting that all things are interconnected and fundamentally one.
Countering Jesuit and Vatican Cosmology
During Poe’s time [and right up to this present moment!], the Jesuits were heavily involved in scientific endeavors, including astronomy and cosmology. The Vatican, influenced by Thomistic philosophy and Aristotelian cosmology, supported a geocentric view for centuries and later accepted the heliocentric model. However, the idea of an eternal and infinite universe was still prevalent.
Poe’s “Eureka” directly challenged these views by proposing a finite universe with a clear beginning, thus countering the notion of an eternal cosmos. Additionally, his suggestion that the universe is self-regulating and will eventually collapse back into a singularity contrasts with the idea of a stable, unchanging universe favored by many religious thinkers.
Challenging the Shape of the Realm and Outer Space
Poe’s cosmology in “Eureka” also delved into the nature of space itself. He rejected the Newtonian concept of absolute space and time, anticipating ideas that would later be more fully developed in Einstein’s theory of relativity. Poe’s universe is dynamic, with space and time intertwined and continuously evolving.
Furthermore, Poe questioned the very nature of what we consider “outer space.” He suggested that space is not an empty void but filled with matter and energy, fundamentally interconnected. This view challenges the traditional separation between the earthly realm and the heavens, a distinction deeply rooted in both religious and scientific thought.
Theoretical Implications
“Eureka” remains a fascinating precursor to many modern cosmological theories. While some of Poe’s ideas were speculative and poetic, they anticipated several key concepts in contemporary cosmology, such as the Big Bang, the finite universe, and the interrelation of space and time. Poe’s work underscores the importance of imaginative and philosophical approaches to understanding the universe, challenging the rigid boundaries of scientific and religious dogma.
Conclusion
Edgar Allan Poe’s “Eureka” stands as a bold and visionary work that defied the cosmological views of his time. By challenging Jesuit and Vatican cosmology and questioning the very nature of the universe, Poe pushed the boundaries of scientific and philosophical thought. “Eureka” remains a testament to Poe’s intellectual curiosity and his willingness to explore the profound mysteries of existence, making it a cornerstone of speculative cosmology.
For further exploration of “Eureka” and its impact on cosmological thought, consider these sources:
- Poe Studies/Dark Romanticism
- The Edgar Allan Poe Society of Baltimore
- Science and Religion: A Historical Introduction